Le Toumelin et al. 2021
In this article, we use the atmospheric model MAR to study how snow storms (driting snow) influence the structure of the atmosphere.
We performed two simulations: one with drifting-snow, one without, and looked at the difference between each other.
When snow blows strongly over the Antarctic continent, snow particles are eroded from the ground and put in suspension in the atmosphere. There, they interact with the environment: they shade the ground during summer, increase the longwave emissions of the amosphere, modify it’s temperature… We argue that they behave very similarly to clouds!
Checkout how a snow storm can modify (according to our model) increase humidity in the atmosphere.
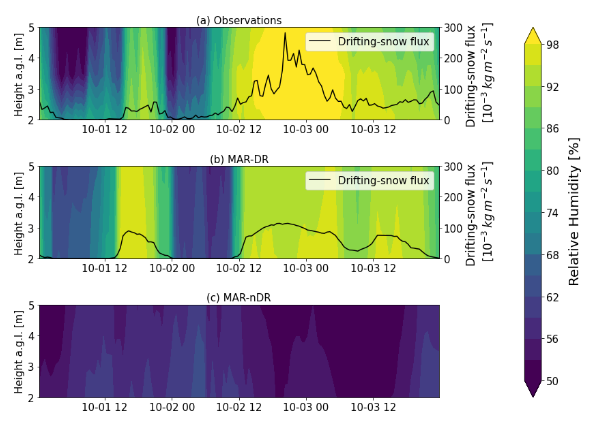
For more info see the full document: https://tc.copernicus.org/articles/15/3595/2021/tc-15-3595-2021.pdf
